NCS and EMG
What is NCS?
NCS stands for Nerve Conduction Studies. These studies measure how long it takes for a nerve impulse to travel along a nerve. If the nerve is trapped, damaged or diseased the signals will be altered. Following some NCS, Electromyography (EMG) may need to be performed. This is a test that records the electrical activity naturally produced in your muscles. You may have one or both of these tests. The tests are used to investigate a number of different muscle and nerve problems and it will assist your consultant in his diagnosis and management of your complaint or condition. The doctor performing the test will explain the procedure before starting.
What do the tests involve?
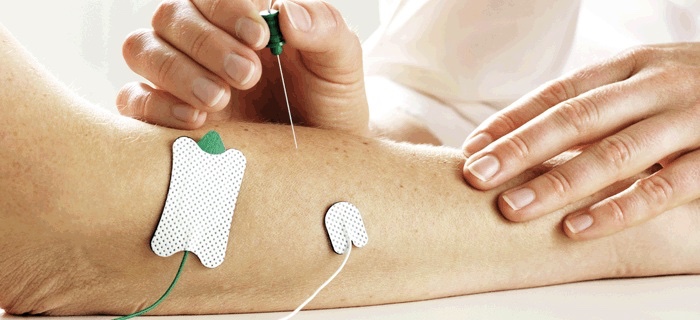
NCS: A number of sticky tabs (electrodes) are placed on the hands or feet. A small electrical pulse is given to the skin, and a measurement taken. This is repeated at 2 or 3 points along the arm or leg. EMG: A fine needle is inserted into a muscle. Recordings are taken with the muscle relaxed and when the muscle is tensed. This takes a few minutes for each muscle.
Who will perform t he test?
A Clinical Physiologist or a doctor will perform NCS. A doctor performs EMG.
Will I feel anything?
NCS: Most people say that the electric pulse is not painful, but that they feel an unusual sensation such as tingling or pulsing. EMG: A fine needle is used for this test, and, although a sharp scratch is felt as the needle is inserted, the majority of our patients do not consider this test to be unduly uncomfortable.
How long will the test take?
NCS: Approximately 30 minutes. EMG: Approximately 20-30 minutes but very occasionally longer. If you require both NCS and EMG the test may take up to 1 hour.
Are there any after-effects following the test?
NCS: No. EMG: The muscles tested may feel sore for a short time after the examination. After both tests you will be able to continue your daily activities as normal. These tests are not a treatment but will help the doctor to understand the reasons for your symptoms.
Are there any risks?
Please tell the doctor if you have a heart pacemaker but it is usually still safe to have the test. NCS: There are no reported risks. EMG: The small size of the needle means that it should not be too uncomfortable. The needle may cause a small amount of bleeding, some bruising and soreness.
When will my consultant get the results?
Your consultant should have the results as soon as possible

 العربية
العربية